Always Encrypted with Secure Enclaves
In this earlier article, I covered the basics and setup steps for Always Encrypted. This post is the follow-up, focusing on Always Encrypted with Secure Enclaves.
In a nutshell, the difference is:
- Classic Always Encrypted — Encryption/decryption happens on the client. SQL Server never sees plaintext, so only
=(with deterministic encryption) is supported; range searches, LIKE, and in-place re-encryption are not. - Always Encrypted with Secure Enclaves — SQL Server evaluates data inside a protected, isolated region (enclave) where values can be decrypted transiently, enabling range queries, LIKE, and in-place encrypt/re-encrypt.
Table of Contents
- What’s different? (Feature comparison)
- Prerequisites (Server / Client)
- Server-side steps (Enable VBS enclave)
- Client-side steps (CMK/CEK & column encryption)
- Validation (previously unsupported queries: PowerShell + ODBC / split)
- Operational security (No attestation / HGS)
- Troubleshooting quick reference
- Summary
1. What’s different? (Feature comparison)
| Item | Classic Always Encrypted | With Secure Enclave |
|---|---|---|
| Where enc/dec happens | Client only | Client + inside the enclave |
| Comparison operators | = only (with deterministic) |
<, >, BETWEEN, IN, etc. supported |
| LIKE search | Not supported | Supported (with some constraints) |
| Re-encryption | Offline/copy based | In-place possible |
2. Prerequisites (Server / Client)
Server (SQL Server)
- SQL Server 2019 or later (Windows; Developer/Enterprise recommended)
- Windows 10 / Windows Server 2019 or later with VBS (Virtualization-Based Security) enabled
Client requirements
Clients must support Always Encrypted with secure enclaves. For ODBC, use ODBC Driver 17.4 or later (18.x recommended for production).
Reference: Microsoft Docs — Using Always Encrypted with the ODBC Driver
Other client stacks (.NET / JDBC, etc.):
Always Encrypted client development (official)
3. Server-side steps (Enable VBS enclave)
- Verify VBS status
Runmsinfo32.exeand check Virtualization-based security is “Running”.
If not (last-resort for testing; proceed at your own risk):# Enable VBS (requires OS restart) Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard' ` -Name EnableVirtualizationBasedSecurity -Value 1 Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard' ` -Name RequirePlatformSecurityFeatures -Value 0 Restart-Computer - Enable the enclave in SQL Server
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; RECONFIGURE; EXEC sp_configure 'column encryption enclave type', 1; -- 1 = VBS enclave RECONFIGURE;Restart the SQL Server service.
- Confirm it’s running
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_column_encryption_enclave; -- 1 row indicates OK
4. Client-side steps (CMK/CEK & column encryption)
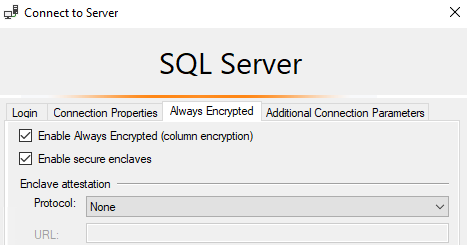
4.1 SSMS connection options
- Connection dialog → Options → Always Encrypted tab
- Turn on Enable Always Encrypted and Enable secure enclaves
- Attestation: choose None for test environments (No attestation)
4.2 Create the certificate (PowerShell / Local Machine store)
Create and store the CMK certificate in the Windows Local Machine certificate store (recommended for operability and service access). Run on the client:
New-SelfSignedCertificate `
-Subject "CN=AlwaysEncryptedCMK" `
-KeySpec KeyExchange `
-KeyLength 2048 `
-CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My"
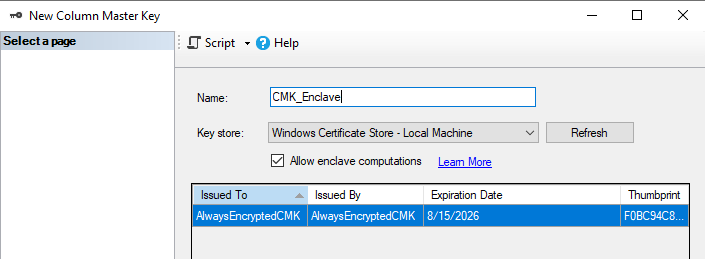
4.3 Create an enclave-enabled CMK (SSMS GUI)
Use SSMS to register an enclave-enabled Column Master Key using the certificate above.
- In the target database: Security → Always Encrypted Keys → right-click Column Master Keys → New Column Master Key.
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
CMK_Enclave). - For Key store, select Windows Certificate Store – Local Machine.
- For Certificate, select the certificate created in 4.2.
- Check Allow enclave computations.
- Click OK to create.
Optional verification:
SELECT name, key_store_provider_name, key_path
FROM sys.column_master_keys;
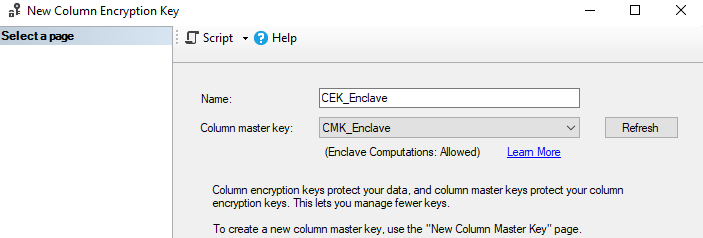
4.4 Create a CEK (SSMS GUI)
Create a Column Encryption Key using the CMK above.
- In SSMS: Always Encrypted Keys → right-click Column Encryption Keys → New Column Encryption Key.
- Enter Name (e.g.,
CEK_Enclave). - Select Column master key =
CMK_Enclave. - Click OK to create.
Optional verification:
SELECT * FROM sys.column_encryption_keys;
4.5 Column encryption (new table or in-place on existing columns)
- New tables: split columns by use case — equality (DETERMINISTIC) vs LIKE (RANDOMIZED + BIN2).
- Existing tables: use the SSMS Encrypt Columns wizard with Use secure enclaves enabled to perform in-place re-encryption.
Example (assumes CEK_Enclave created in 4.4):
CREATE TABLE dbo.Patients (
PatientId int IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
-- Equality (=): DETERMINISTIC + BIN2
SSN_EQ char(11) COLLATE Latin1_General_BIN2
ENCRYPTED WITH (
ENCRYPTION_TYPE = DETERMINISTIC,
ALGORITHM = 'AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_256',
COLUMN_ENCRYPTION_KEY = CEK_Enclave
) NOT NULL,
-- LIKE: RANDOMIZED + BIN2
SSN_LIKE char(11) COLLATE Latin1_General_BIN2
ENCRYPTED WITH (
ENCRYPTION_TYPE = RANDOMIZED,
ALGORITHM = 'AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_256',
COLUMN_ENCRYPTION_KEY = CEK_Enclave
) NOT NULL,
-- Range queries (BETWEEN, etc.): date column (RANDOMIZED is fine with enclave evaluation)
BirthDate date
ENCRYPTED WITH (
ENCRYPTION_TYPE = RANDOMIZED,
ALGORITHM = 'AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_256',
COLUMN_ENCRYPTION_KEY = CEK_Enclave
) NULL
);
4.6 App/tool connection strings (ODBC)
Use the enclave protocol rather than the legacy Column Encryption Setting=Enabled.
# Testing (No attestation)
Driver={ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server};
Server=HOST\INSTANCE;Database=YourDB;Encrypt=yes;Trusted_Connection=yes;
ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE
# Production (attestation with HGS)
...; ColumnEncryption=VBS-HGS,http://<HGS-server>/Attestation
5. Validation (previously unsupported queries: PowerShell + ODBC / split)
Use System.Data.Odbc from PowerShell with ODBC Driver 17.4+ (18.x recommended).
Specify ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE for test setups and always use parameterized queries.
5.1 INSERT
$server = "HOST\INSTANCE"
$database = "YourDB"
$cs = @"
Driver={ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server};
Server=$server;Database=$database;Encrypt=yes;TrustServerCertificate=yes;
Trusted_Connection=yes;ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE
"@
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Data
$cn = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection($cs)
$cn.Open()
# INSERT (columns: SSN_EQ, SSN_LIKE, BirthDate)
$sql = "INSERT INTO dbo.Patients(SSN_EQ, SSN_LIKE, BirthDate) VALUES(?, ?, ?);"
$cmd = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcCommand($sql, $cn)
$p1 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p1.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Char; $p1.Size = 11; $p1.Value = "123-45-6789"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p1)
$p2 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p2.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Char; $p2.Size = 11; $p2.Value = "123-45-6789"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p2)
$p3 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p3.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Date; $p3.Value = [DateTime]"1985-04-12"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p3)
[void]$cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
$cmd.Dispose()
$cn.Close(); $cn.Dispose()
5.2 SELECT (range: BETWEEN)
$server = "HOST\INSTANCE"
$database = "YourDB"
$cs = @"
Driver={ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server};
Server=$server;Database=$database;Encrypt=yes;TrustServerCertificate=yes;
Trusted_Connection=yes;ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE
"@
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Data
$cn = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection($cs)
$cn.Open()
$sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM dbo.Patients WHERE BirthDate BETWEEN ? AND ?;"
$cmd = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcCommand($sql, $cn)
$p1 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p1.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Date; $p1.Value = [DateTime]"1980-01-01"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p1)
$p2 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p2.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Date; $p2.Value = [DateTime]"1995-12-31"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p2)
$cnt = $cmd.ExecuteScalar()
"Rows in range (1980-01-01 to 1995-12-31): $cnt" | Write-Host
$cmd.Dispose()
$cn.Close(); $cn.Dispose()
5.3 SELECT (LIKE: prefix match)
SSN_LIKE must be RANDOMIZED + BIN2.
$server = "HOST\INSTANCE"
$database = "YourDB"
$cs = @"
Driver={ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server};
Server=$server;Database=$database;Encrypt=yes;TrustServerCertificate=yes;
Trusted_Connection=yes;ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE
"@
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Data
$cn = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection($cs)
$cn.Open()
$sql = "SELECT PatientId, SSN_LIKE, BirthDate FROM dbo.Patients WHERE SSN_LIKE LIKE ?;"
$cmd = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcCommand($sql, $cn)
$p1 = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcParameter
$p1.OdbcType = [System.Data.Odbc.OdbcType]::Char; $p1.Size = 11; $p1.Value = "123-45-%"; [void]$cmd.Parameters.Add($p1)
$da = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcDataAdapter($cmd)
$dt = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
[void]$da.Fill($dt)
"LIKE results (SSN_LIKE LIKE '123-45-%'):" | Write-Host
$dt | Format-Table -AutoSize
$cmd.Dispose(); $da.Dispose()
$cn.Close(); $cn.Dispose()
Key points:
- Use
ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONEfor test; useVBS-HGS,<URL>for production attestation. - Parameters must be added in the exact order of the ? placeholders (names are ignored by ODBC).
- Match data types precisely: use
OdbcType.Datefordatecolumns; useOdbcType.CharandSizefor fixed-length strings. - LIKE requires a RANDOMIZED + BIN2 string column (e.g.,
SSN_LIKE).
6. Operational security (No attestation / HGS)
- No attestation (testing): skip attestation; simpler to set up but no tamper detection.
- With HGS (Host Guardian Service): clients attest the enclave’s health with a third party (HGS) before releasing keys.
- Common key stores: Windows Certificate Store (Local Machine) and Azure Key Vault.
7. Troubleshooting quick reference
- DMV returns 0 rows (
sys.dm_column_encryption_enclave): VBS not running /sp_configurenot applied / forgot to restart. - “Allow enclave computations” not visible: didn’t enable Enable secure enclaves on connection and/or enclave not enabled on the server.
- Connection string issues: must specify
ColumnEncryption=VBS-NONE(orVBS-HGS,<URL>).
8. Summary
- Secure Enclaves enable server-side evaluation (range/LIKE/in-place re-encryption) while preserving confidentiality.
- Start with No attestation for a quick POC, then add HGS (and optionally AKV) as you move toward production.
- Read this together with the earlier post on classic Always Encrypted for the full picture.
