This guide is designed for those installing and operating SQL Server for the first time.
We will cover everything from choosing the right edition and GUI installation to network configuration, SQL Server Agent, updates (CU/GDR), and setting up SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio), complete with diagrams and step-by-step procedures.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction: What is SQL Server?
1.1 Overview and Role
SQL Server (Microsoft SQL Server) is a commercial Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It integrates high-speed OLTP (Online Transaction Processing), data analysis, robust security, backup solutions, and high availability.
It is known for its high compatibility with Windows Server and its powerful management tool, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
1.2 Features of an RDBMS
- Structured Data: Manages data in tables (rows and columns) and manipulates it using SQL.
- Data Integrity: Strong support for constraints and ACID transactions (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
- Versatility: Widely used in core business systems, E-commerce, finance, healthcare, and BI/Analytics.
RDBMS Concept Diagram
┌──────────────────────┐
│ Application │
│ (Web/Business/BI) │
└─────┬────────────────┘
│ SQL (SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE)
┌─────▼────────────────┐
│ SQL Server (RDBMS) │
│ - Transactions (ACID)│
│ - Optimization/Stats │
│ - Security/Backup │
└─────┬────────────────┘
│ Data/Log I/O
┌─────▼────────────────┐
│ Storage (Data/Log) │
└──────────────────────┘1.3 Free Editions (Developer / Express)
- Developer: Includes all features of the Enterprise edition. It is free for development and testing purposes but cannot be used in production environments.
- Express: A free, lightweight edition for production use. It has limitations such as a 10GB database size limit and caps on CPU/Memory usage.
2. Choosing an Edition
2.1 Edition Comparison
| Feature | Enterprise | Standard | Express | Developer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Large Scale / High Availability | Medium Scale / General Business | Small Scale / Learning | Dev / Test (No Production) |
| Compute Limit | OS Maximum | 4 Sockets or 24 Cores | 1 Socket or 4 Cores | OS Maximum |
| Memory Limit | OS Maximum | 128 GB | Approx. 1.41 GB | OS Maximum |
| Max DB Size | 524 PB | 524 PB | 10 GB | 524 PB |
| High Availability | Always On (Full) | Basic AG | None | Always On (Test only) |
2.2 Recommendations by Use Case
- Learning / Development: Choose Developer (Full features, free).
- Small Apps: Choose Express (Be mindful of the 10GB limit).
- Medium Business: Choose Standard (Balance of cost and features).
- Mission Critical: Choose Enterprise.
3. Installation Guide (GUI)
3.1 Download and Preparation
- Access the official download page and click “Download now” for your chosen edition:
SQL Server Downloads | MicrosoftGet started with Microsoft SQL Server downloads. Choose a SQL Server trial, edition, tool, or connector that best meets ... - Run the downloaded executable file (e.g.,
SQL2025-SSEI-EntDev.exe). - Select “Download Media”.
- Select “ISO” and click “Download”.
- Once completed, mount the ISO file or extract it to prepare for installation.
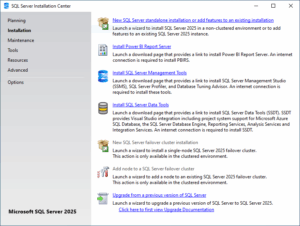
3.2 Installation Wizard Steps
Installation Flow (GUI)
[Launch setup.exe] → New SQL Server stand-alone installation
├─ License Terms
├─ Global Rules
├─ Microsoft Updates
├─ Product Update
├─ Install Setup Files
├─ Install Rules
├─ Azure Extension for SQL Server
├─ Feature Selection
├─ Feature Rules
├─ Feature Configuration Rules
├─ Ready to install
├─ Installation Progress
└─ CompleteDuring the installation of SQL Server, you will configure several key options. It is crucial to understand which settings are permanent and which can be changed later.
| Setting | Description | Changeable Later? |
|---|---|---|
| Instance Name | The name of the SQL Server instance (e.g., MSSQLSERVER or MyInstance). | NO (Requires Re-installation) |
| Install Directory | The physical path for binary files. | NO (Requires Re-installation) |
| Edition | The license type (e.g., Developer, Standard, Enterprise). | Upgrade Only (You can upgrade to a higher edition, but cannot downgrade without re-installing.) |
| Data File Location | Default path for user database files (.mdf, .ldf). | YES (Can be changed in Server Properties.) |
| Installed Features | Components like Replication, Machine Learning Services, etc. | YES (You can add features later by running setup again.) |
| Memory Allocation | Max server memory. | YES (Can be changed anytime.) |
| Authentication Mode | Windows Authentication vs. Mixed Mode. | YES (Can be switched anytime.) |
Key Steps requiring your attention:
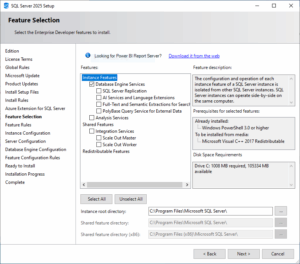
1. Feature Selection: Choose “Database Engine Services” for the core database functionality.
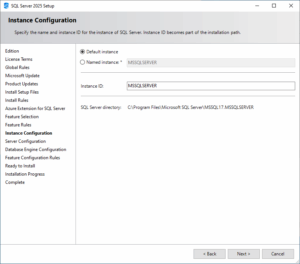
2. Instance Configuration: Choose “Default Instance” if this is your first SQL Server on this machine.
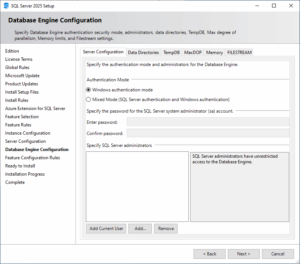
3. Database Engine Configuration (Authentication): Select “Mixed Mode” and don’t forget to click “Add Current User” to make yourself an administrator.
3.3 Post-Installation Verification
Open SSMS (see Section 7) or a command line tool and run the following query to check the version:
SELECT @@VERSION;
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS ProductVersion,
SERVERPROPERTY('ProductLevel') AS ProductLevel,
SERVERPROPERTY('Edition') AS Edition,
SERVERPROPERTY('EngineEdition') AS EngineEdition;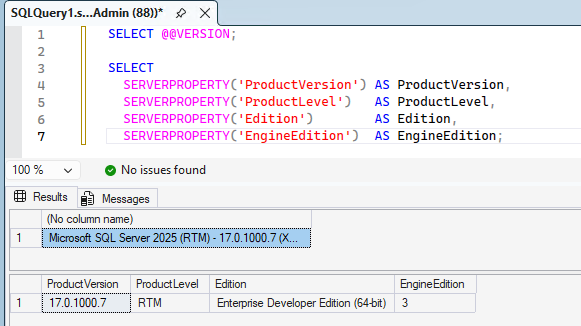
4. Basic Management Operations
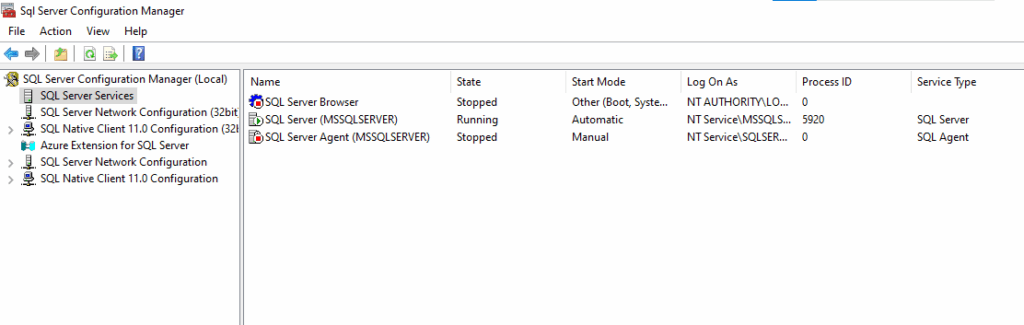
4.1 Managing Services (Configuration Manager)
Use “SQL Server Configuration Manager” to manage services. Do not use the standard Windows Services console if possible.
Here you can start/stop SQL Server, SQL Server Agent, and SQL Server Browser.
4.2 Network Configuration (TCP/IP, Ports)
In Configuration Manager, expand SQL Server Network Configuration > Protocols for [Instance].
- Enable TCP/IP: It is often disabled by default on Developer/Express editions. Right-click and select “Enable”.
- Ports: Default instances use TCP 1433. Named instances use dynamic ports, requiring the SQL Browser service (UDP 1434).
Connection Concept
Client
│ TCP 1433 (Default) / Static Port / Named: SQL Browser (UDP 1434)
▼
SQL Server (Default or Named)
├─ Default: SERVER:1433
└─ Named: SERVER\INSTANCE (Dynamic Port)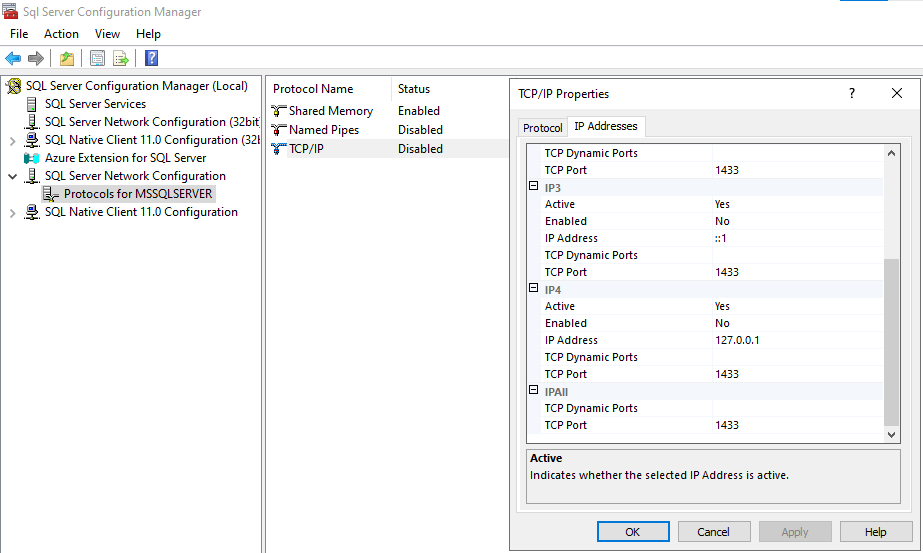
Firewall Settings (PowerShell Example)
If you need to open ports on the Windows Firewall:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "SQL Server TCP 1433" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 1433
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "SQL Browser UDP 1434" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol UDP -LocalPort 14344.3 SQL Server Agent
- Used for scheduling jobs (Backups, Index maintenance, etc.).
- Note: SQL Server Agent is not available in the Express edition.
5. Applying Updates (CU/GDR)
5.1 What are CU and GDR?
- CU (Cumulative Update): Contains all previous updates plus new bug fixes and feature enhancements. Recommended for most users.
- GDR (General Distribution Release): Contains only critical security updates.
5.2 How to Apply Updates
- Identify the latest CU/GDR for your version.
- Backup your databases.
- Download and run the update installer.
- Follow the wizard to update the instance.
5.3 Important Considerations
- Updates may require a restart.
- Always backup system databases (master, msdb, model) and user databases before patching.
5.4 Checking for Updates
Bookmark the official Microsoft Build Versions page to stay informed about the latest releases.
6. Uninstallation
6.1 How to Uninstall an Instance
- Stop all SQL Server related services.
- Go to Windows Settings > Apps & features.
- Select “Microsoft SQL Server (Version) (Bit)” and click Uninstall.
- Select “Remove” and choose the instance you want to delete.
- Warning: This does not delete your database files (.mdf/.ldf). Manually back up or delete the data folders if they are no longer needed.
7. Installing and Connecting with SSMS
7.1 Role of SSMS
SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio) is the primary GUI tool for managing SQL Server. You can create databases, execute queries, configure security, and manage jobs.
7.2 Download and Installation
Since SQL Server 2016, SSMS is installed separately from the database engine.
- Download the latest version from the official Microsoft site.
- Run the installer. No complex configuration is required.
7.3 Connecting to SQL Server
Launch SSMS and you will see the “Connect to Server” dialog.
SSMS Connection Dialog
+------------------------------+
| Server name: SERVER\INSTANCE|
| Authentication: Windows/SQL |
| User name: (If SQL Auth) |
| Password: (If SQL Auth) |
| [Connect] |
+------------------------------+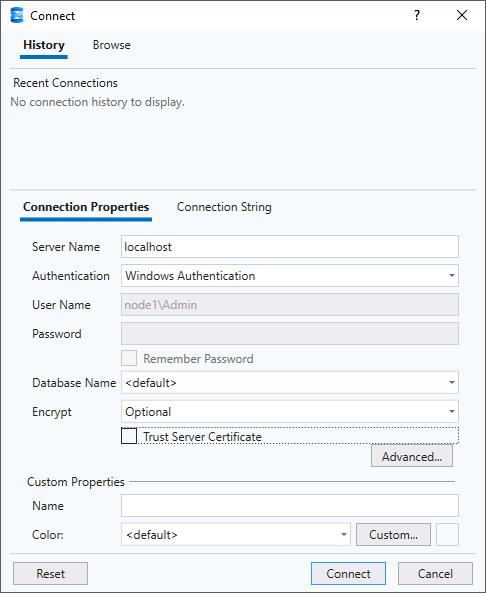
- Server name: Use
localhostor.for a local default instance. Use.\INSTANCE_NAMEfor a local named instance. - Authentication: Use Windows Authentication if you are logged in to the machine.
- Encrypt: Encrypt is set to Mandatory by default, so change it to Optional. If it remains Mandatory, an encrypted connection will be attempted, which will fail by default.
This concludes the Setup guide (No.1).
