1. Reference to the Previous Security Blog
In the previously introduced blog post
Understanding SQL Server Security Features (DBA park),
several key SQL Server security features were discussed. Among them was
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), described as follows:
- Purpose: Encrypts the entire database files (.mdf/.ldf) and backup files
- Use case: Ideal for protecting data stored on disk or in backup media
- Limitation: Does not encrypt data in memory or during transmission
2. Features and Limitations of TDE
Features
- Encrypts data files (.mdf/.ndf), log files (.ldf), and backup files as a whole
- Encryption is transparent to applications—no changes to queries or code are required
- tempdb is automatically encrypted when TDE is enabled for any user database
- Secure key hierarchy: DEK → Certificate → Master Key → SMK (via DPAPI)
Limitations & Considerations
- Protects data at rest only; does not encrypt in-memory data or network traffic
- Edition requirements:
- SQL Server 2017: Enterprise / Developer only
- SQL Server 2019 and later: Available in Standard edition
- Certificate and key backups are mandatory—losing them makes database recovery impossible
- Encryption runs in the background—progress should be monitored
- For Always On / Log Shipping, the certificate must be deployed to secondary servers as well
3. Steps to Enable TDE
Example: Create a new database tdeTest and enable TDE.
① Create the Master Key (in the master database)
USE master;
GO
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P@ssw0rd';
GO
② Create a Server Certificate for TDE
USE master;
GO
CREATE CERTIFICATE TDE_ServerCert
WITH SUBJECT = 'TDE Certificate';
GO
③ Back Up the Certificate (Mandatory)
BACKUP CERTIFICATE TDE_ServerCert
TO FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert.cer'
WITH PRIVATE KEY (
FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert_PrivateKey.pvk',
ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P@ssw0rd'
);
④ Create the Database
CREATE DATABASE tdeTest;
GO
⑤ Create the Database Encryption Key (DEK) and Protect it with the Certificate
USE tdeTest;
GO
CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY
WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256
ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE TDE_ServerCert;
GO
⑥ Enable Encryption
ALTER DATABASE tdeTest
SET ENCRYPTION ON;
GO
4. How to Verify TDE is Enabled (Using a Hex Editor)
Check within SQL Server
SELECT
db_name(database_id) AS database_name,
encryption_state,
percent_complete,
key_algorithm,
key_length
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys
WHERE database_id = DB_ID('tdeTest');
If encryption_state = 3, encryption is complete.
Meaning of encryption_state values
| encryption_state | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No database encryption key present | No DEK exists; TDE is not configured. |
| 1 | Unencrypted | DEK exists but the database is not encrypted. |
| 2 | Encryption in progress | Encryption is currently being applied in the background. |
| 3 | Encrypted | The database is fully encrypted (TDE enabled). |
| 4 | Key change in progress | DEK is being regenerated or rotated. |
| 5 | Decryption in progress | Database is being decrypted (TDE being disabled). |
| 6 | Protection change in progress | Changing the protection of the DEK (e.g., to a different certificate). |
Visual Verification Using a Hex Editor
Below is a practical step-by-step method to visually confirm whether TDE is working. This process requires access to the database files and should be done in a test environment.
- Download a hex editor
– Windows: HxD (Free)
– macOS: Hex Fiend (Free) - Disable TDE on the target database (if enabled), create a test table, and insert a known value:
ALTER DATABASE tdeTest SET ENCRYPTION OFF; GO CREATE TABLE TestTable (id varchar(100)); INSERT INTO TestTable VALUES ('abcdefg'); GO - Stop the SQL Server instance, open the database file (.mdf) in the hex editor, and confirm that the string “abc” is visible in plain text.
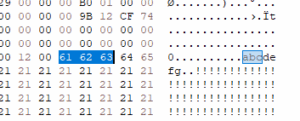
- Enable TDE on the database using the steps above.
- Stop the instance again, reopen the database file in the hex editor, and confirm that the string “abc” is no longer readable (it should appear as garbled binary data).
Note: Never perform this directly on a production database. Always work from backups or a dedicated test environment to avoid data corruption.
5. Restoring a TDE-Encrypted Database to Another SQL Server Instance
When restoring a TDE-encrypted database to another SQL Server instance, you must first restore the server certificate and private key that were used to protect the database encryption key (DEK) on the source server. Without these, the restore will fail with an error similar to Cannot find server certificate with thumbprint....
Step-by-step process:
- Back up the certificate and private key on the source server (should already be done when enabling TDE):
USE master; GO BACKUP CERTIFICATE TDE_ServerCert TO FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert.cer' WITH PRIVATE KEY ( FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert_PrivateKey.pvk', ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P@ssw0rd' ); - Copy the certificate and private key files (
.cerand.pvk) to the target server in a secure manner. - Create the master key on the target server (if it does not exist):
USE master; GO CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P@ssw0rd'; GO - Restore the certificate and private key on the target server:
USE master; GO CREATE CERTIFICATE TDE_ServerCert FROM FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert.cer' WITH PRIVATE KEY ( FILE = 'C:\TDE_ServerCert_PrivateKey.pvk', DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P@ssw0rd' ); GO - Restore the TDE-encrypted database backup:
RESTORE DATABASE tdeTest FROM DISK = 'C:\backup\tdeTest.bak' WITH MOVE 'tdeTest' TO 'C:\MSSQL\Data\tdeTest.mdf', MOVE 'tdeTest_log' TO 'C:\MSSQL\Data\tdeTest.ldf', REPLACE; GO
Important Notes:
- Always store certificate backups (.cer and .pvk) in a secure location, separate from the database backups.
- If the certificate and key are lost, the encrypted database cannot be restored anywhere.
- For high availability features like Always On or Log Shipping, this certificate setup must be done on all secondary replicas.
